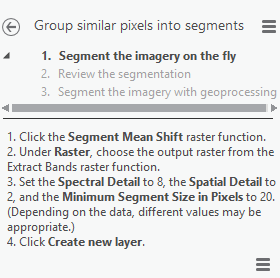
For this lab we will use the Pix4D processing software to process data taken from a phantom drone at Litchfield. We processed this data last week but this time we will process the data using Ground Control Points. This will yield highly accurate Pix4D maps that will create DSM maps of higher quality.
Methods
First you will need to open up Pix4D and at the images you wish to process. Once you have the images loaded into Pix4D you may add in GCPs using the GCP manager.
After you add in your GCPs you need to make sure that your Y coordinates are Northings and your X coordinates are the eastings. You may then do the initial processing of the data. After the initial processing is completed you will notice that the GCPs are not tied down to the ground.
We will now go through the process of placing the GCPs in the correct locations. First go to the Map and click on GCPs until you find point 0. When you click on a GCP it will bring up the GCP manager.
We will then select basic editor to add the correct locations for GCPs. Once you open the basic editor you will go through a few images, 2-5, where you can clearly see the GCPs.
You will point your cursor on the GCP in the image to tie it to this location. You will do this for 4 or 5 different GCPs and then re optimize your image.
After you do this for about 5 GCPs you can reoptimize the image This will allow you to more easily tie down the GCPs. You will have a group of images pop on the left hand side once you select a GCP from the layers column. From here you can correctly place the target on the GCP. You will notice some are close to the GCP but do not directly fall on the target. Once you do two or three you can select automatic marking and it will do the rest of the images for you. You will do this for all the GCPs that fall within the specific flight log.
After you complete this step all the GCPs should be tied to the ground and you can begin the steps 2 and 3 of processing.
After you finish steps two and three of processing you will end up with a raycloud map that has GCPs tied down.
Once you have both projects processed and tied down. You can create a new project that will merge both projects into one. Since the GCPs are all tied down this processing should complete slightly faster. If everything is tied down correctly the maps should perfectly overlay each other and GCPs should be tied down correctly.
Results
The merged DSM file within ArcMap should turn out pretty good if all your GCPs are tied down correctly. The final project will look something similar to figure 1. The map turns out a lot more accurate when compared to the basemap. There are some locations where the data on the maps is skewed. This would be in the south east corner of the map. This is the area of vegetation from the forest so this makes sense as to why the DSM file looks weird here.You notice the highest elevation within the map are areas to the northeast and the large piles of material through throughout the mapping area. The lake seems to be the area of lowest elevation which also makes sense. The GCPs allow us to easily connect separate flights into one data that overlay each other correctly. The Pix4D software seems to be very user friendly. It may be time consuming but easy to use. If you tie down the GCPs correctly you should run into little problems.
 |
| Figure 1 |